Appearance
算法题
问题 1:还原一棵树
实现 buildTree 方法
js
const list = [
{ id: "a2", label: "1", pid: "a1" },
{ id: "a3", label: "2", pid: "a17" },
{ id: "a1", label: "3", pid: "root" },
{ id: "a4", label: "4", pid: "a3" },
{ id: "a5", label: "5", pid: "a4" },
{ id: "ax", label: "6", pid: "a5" },
{ id: "ay", label: "7", pid: "a5" },
{ id: "a6", label: "8", pid: "a4" },
{ id: "a7", label: "9", pid: "a6" },
{ id: "a9", label: "10", pid: "a7" },
{ id: "a10", label: "11", pid: "a9" },
{ id: "a11", label: "12", pid: "a10" },
{ id: "a12", label: "13", pid: "a10" },
{ id: "a13", label: "14", pid: "a10" },
{ id: "a14", label: "15", pid: "a11" },
{ id: "a15", label: "16", pid: "a12" },
{ id: "a16", label: "17", pid: "a13" },
{ id: "a17", label: "18", pid: "a2" },
];
function buildTree(node, list) {}
const tree = buildTree({ id: "root", name: "root", pid: null }, list);
console.log(JSON.stringify(tree));解析:
js
function buildTree(node, list) {
const children = list.filter((item) => item.pid === node.id);
if (children.length > 0) {
node.children = children.map((item) => buildTree(item, list));
}
return node;
}问题 2:合并排序
给定两个已排序(升序)好的数组,将两个数组合并为一个新的数组,并使新数组仍然有序
js
function mergeSort(arr1, arr2) {}
console.log(mergeSort([1, 3, 5], [2, 4, 6, 8])); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8]解析:双指针
md
⬇️
1, 3, 5
2, 4, 6
⬆️
result = []
比较两个指针的值,小的放入 result 中,指针后移js
function mergeSort(arr1, arr2) {
// arr1的指针
let p1 = 0;
// arr2的指针
let p2 = 0;
// 存放最后排序结果的数组
const result = [];
while (p1 < arr1.length || p2 < arr2.length) {
if (arr1[p1] < arr2[p2]) {
// arr1[i] 比 arr2[j] 小
result.push(arr1[p1]);
p1++;
} else if (arr1[p1] > arr2[p2]) {
// arr1[i] 比 arr2[j] 大
result.push(arr2[p2]);
p2++;
} else if (p1 >= arr1.length) {
// arr1已经走完,将arr2剩余内容放入result中
result.push(arr2[p2]);
p2++;
} else if (p2 >= arr2.length) {
// arr2已经走完,将arr1剩余内容放入result中
result.push(arr1[p1]);
p1++;
}
}
return result;
}
console.log(mergeSort([1, 3, 5], [2, 4, 6, 8])); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8]问题 3:使用自定义上下文调用函数(手写 call)
增强所有函数,使其具有 callPolyfill 方法。该方法接受一个对象 obj 作为第一个参数,以及任意数量的附加参数。obj 成为函数的 this 上下文。附加参数将传递给该函数(即 callPolyfill 方法所属的函数)。
例如,如果有以下函数:
js
function tax(price, taxRate) {
const totalCost = price * (1 + taxRate);
console.log(`The cost of ${this.item} is ${totalCost}`);
}调用 tax(10, 0.1) 将输出 "The cost of undefined is 11" 。这是因为 this 上下文未定义。
然而,调用 tax.callPolyfill({item: "salad"}, 10, 0.1) 将输出 "The cost of salad is 11" 。this 上下文被正确设置,函数输出了适当的结果。
请在不使用内置的 Function.call 方法的情况下解决这个问题。
解析:
js
Function.prototype.callPolyfill = function (context, ...args) {
ctx = context || window;
const key = Symbol();
ctx[key] = this;
const result = ctx[key](...args);
delete ctx[key];
return result;
};拓展:
js
// 手写apply 跟call类似,只是参数不同,apply 参数是一个数组
Function.prototype.myApply = function (context, args) {
const fn = this;
const key = Symbol();
context = context || window;
context[key] = fn;
const result = context[key](...args);
delete context[key];
return result;
};
// 手写bind
Function.prototype.myBind = function (context, ...args) {
const fn = this;
return function (...innerArgs) {
return fn.call(context, ...args, ...innerArgs);
};
};问题 4:排序方式
给定一个数组 arr 和一个函数 fn,返回一个排序后的数组 sortedArr。你可以假设 fn 只返回数字,并且这些数字决定了 sortedArr 的排序顺序。sortedArr 必须按照 fn 的输出值 升序 排序。
你可以假设对于给定的数组,fn 不会返回重复的数字。 解析:
js
/**
* @param {Array} arr
* @param {Function} fn
* @return {Array}
*/
var sortBy = function(arr, fn) {
return arr.sort((acc, cur) => fn(acc) - fn(cur));
};
不使用sort:冒泡(性能不佳)
var sortBy = function(arr, fn) {
const result =[...arr];
for (let i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < result.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (fn(result[j]) > fn(result[j + 1])) {
[result[j], result[j + 1]] = [result[j + 1], result[j]];
}
}
}
return result;
}问题 5: 转换数组中的每个元素
编写一个函数,这个函数接收一个整数数组 arr 和一个映射函数 fn ,通过该映射函数返回一个新的数组。
返回数组的创建语句应为 returnedArray[i] = fn(arr[i], i) 。
请你在不使用内置方法 Array.map 的前提下解决这个问题。
解析:
js
/**
* @param {number[]} arr
* @param {Function} fn
* @return {number[]}
*/
var map = function (arr, fn) {
return arr.reduce((pre, item, i) => {
pre.push(fn(item, i));
return pre;
}, []);
};
var map2 = function (arr, fn) {
let returnedArray = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
returnedArray[i] = fn(arr[i], i);
}
return returnedArray;
};问题 6:执行可取消的延迟函数
给定一个函数 fn ,一个参数数组 args 和一个以毫秒为单位的超时时间 t ,返回一个取消函数 cancelFn 。
在 cancelTimeMs 的延迟后,返回的取消函数 cancelFn 将被调用。
setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs) 最初,函数 fn 的执行应该延迟 t 毫秒。
如果在 t 毫秒的延迟之前调用了函数 cancelFn,它应该取消 fn 的延迟执行。否则,如果在指定的延迟 t 内没有调用 cancelFn,则应执行 fn,并使用提供的 args 作为参数。
解析:
js
/**
* @param {Function} fn
* @param {Array} args
* @param {number} t
* @return {Function}
*/
var cancellable = function (fn, args, t) {
let timer = setTimeout(() => fn(...args), t);
return function cancel() {
clearTimeout(timer);
};
};问题 7: 计数器
给定一个整型参数 n,请你编写并返回一个 counter 函数。这个 counter 函数最初返回 n,每次调用它时会返回前一个值加 1 的值 ( n , n + 1 , n + 2 ,等等)。 解析:
js
var createCounter = function (n) {
return function () {
return ++n;
};
};问题 8: 根据 ID 合并两个数组
现给定两个数组 arr1 和 arr2 ,返回一个新的数组 joinedArray 。两个输入数组中的每个对象都包含一个 id 字段。
joinedArray 是一个通过 id 将 arr1 和 arr2 连接而成的数组。joinedArray 的长度应为唯一值 id 的长度。返回的数组应按 id 升序 排序。
如果一个 id 存在于一个数组中但不存在于另一个数组中,则该对象应包含在结果数组中且不进行修改。
如果两个对象共享一个 id ,则它们的属性应进行合并:
如果一个键只存在于一个对象中,则该键值对应该包含在对象中。 如果一个键在两个对象中都包含,则 arr2 中的值应覆盖 arr1 中的值。
解析
js
/**
* @param {Array} arr1
* @param {Array} arr2
* @return {Array}
*/
var join = function (arr1, arr2) {
const map = new Map();
arr1.concat(arr2).forEach((item) => {
map.set(item.id, {
...map.get(item?.id),
...item,
});
});
return [...map.values()].sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id);
// 方式一:普通方式超时:
// let joinedArray = [...arr1];
// arr2.forEach((item) => {
// const index = arr1.findIndex((x) => x.id === item.id);
// if (index === -1) {
// joinedArray.push(item);
// } else {
// joinedArray[index] = {
// ...joinedArray[index],
// ...item,
// };
// }
// });
// return joinedArray.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id);
// 方式二:
// const map = new Map(arr1.map((item) => [item.id, item]));
// arr2.forEach((item) => {
// if (map.has(item.id)) {
// const oldItem = map.get(item.id);
// map.set(item.id, { ...oldItem, ...item });
// } else {
// map.set(item.id, item);
// }
// });
// return [...map.values()].sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id);
};问题 9: 手写 Promise
js
const PENDING = "pending";
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MyPromise {
#_status = PENDING;
#_result;
#thenables = [];
constructor(executor) {
const resolve = (data) => {
// console.log("resolve", data);
this.#changeStatus(FULFILLED, data);
};
const reject = (reason) => {
// console.log("reject", reason);
this.#changeStatus(REJECTED, reason);
};
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
// 状态一旦改变就不能再改变
#changeStatus(status, result) {
if (this.#_status !== "pending") return;
this.#_status = status;
this.#_result = result;
this.#run();
}
#handleCallback(callback, resolve, reject) {
if (typeof callback !== "function") {
queueMicrotask(() => {
const settled = this.#_status === FULFILLED ? resolve : reject;
settled(this.#_result);
});
return;
}
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
const result = callback(this.#_result);
if (result instanceof MyPromise || result instanceof Promise) {
result.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
}
#run() {
if (this.#_status === PENDING) return;
while (this.#thenables.length) {
const { onFulfilled, onRejected, resolve, reject } =
this.#thenables.shift();
if (this.#_status === FULFILLED) {
this.#handleCallback(onFulfilled, resolve, reject);
} else {
this.#handleCallback(onRejected, resolve, reject);
}
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.#thenables.push({
onFulfilled,
onRejected,
resolve,
reject,
});
this.#run();
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
return this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
return this.then(
(value) => {
onFinally();
return value;
},
(reason) => {
onFinally();
throw reason;
}
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new MyPromise((resolve) => resolve(value));
}
}问题 10: 嵌套数组生成器
现给定一个整数的 多维数组 ,请你返回一个生成器对象,按照 中序遍历 的顺序逐个生成整数。
多维数组 是一个递归数据结构,包含整数和其他 多维数组。
中序遍历 是从左到右遍历每个数组,在遇到任何整数时生成它,遇到任何数组时递归应用 中序遍历 。
解析
js
/**
* @param {Array} arr
* @return {Generator}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function* (arr) {
if (!arr.length) return;
const getArrayFistValue = (array) => {
let value = [];
array?.forEach((item) => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
value = [...value, ...getArrayFistValue(item)];
} else {
value.push(item);
}
});
return value;
};
for (const item of getArrayFistValue(arr)) {
yield item;
}
// 扁平化 方式
// const nums = arr.flat(Infinity);
// for (const item of nums) {
// yield item;
// }
};问题 11: 蜗牛排序
请你编写一段代码为所有数组实现 snail(rowsCount,colsCount) 方法,该方法将 1D 数组转换为以蜗牛排序的模式的 2D 数组。无效的输入值应该输出一个空数组。当 rowsCount * colsCount !==nums.length 时。这个输入被认为是无效的。
蜗牛排序从左上角的单元格开始,从当前数组的第一个值开始。然后,它从上到下遍历第一列,接着移动到右边的下一列,并从下到上遍历它。将这种模式持续下去,每列交替变换遍历方向,直到覆盖整个数组。例如,当给定输入数组 [19, 10, 3, 7, 9, 8, 5, 2, 1, 17, 16, 14, 12, 18, 6, 13, 11, 20, 4, 15] ,当 rowsCount = 5 且 colsCount = 4 时,需要输出矩阵如下图所示。注意,矩阵沿箭头方向对应于原数组中数字的顺序 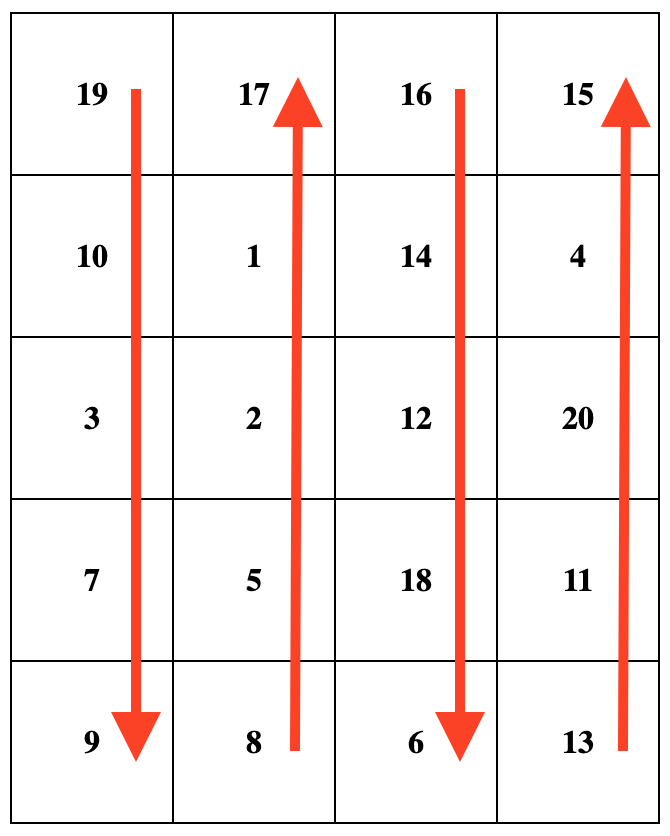 输入: nums = [19, 10, 3, 7, 9, 8, 5, 2, 1, 17, 16, 14, 12, 18, 6, 13, 11, 20, 4, 15] rowsCount = 5 colsCount = 4 输出: [ [19,17,16,15], [10,1,14,4], [3,2,12,20], [7,5,18,11], [9,8,6,13] ]
输入: nums = [19, 10, 3, 7, 9, 8, 5, 2, 1, 17, 16, 14, 12, 18, 6, 13, 11, 20, 4, 15] rowsCount = 5 colsCount = 4 输出: [ [19,17,16,15], [10,1,14,4], [3,2,12,20], [7,5,18,11], [9,8,6,13] ]
解析
js
/**
* @param {number} rowsCount
* @param {number} colsCount
* @return {Array<Array<number>>}
*/
Array.prototype.snail = function (rowsCount, colsCount) {
const arr = this;
if (rowsCount * colsCount !== arr.length) return [];
let result = [];
let curRowIndex = 0;
let curColIndex = 0;
let curDir = "down";
const nextDir = () => {
curColIndex++;
curDir = curDir === "down" ? "up" : "down";
};
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (result[curRowIndex] === undefined) {
result[curRowIndex] = [];
}
result[curRowIndex][curColIndex] = arr[i];
if (curDir === "down") {
curRowIndex++;
} else {
curRowIndex--;
}
if (curRowIndex === rowsCount) {
nextDir();
curRowIndex -= 1;
}
if (curRowIndex === -1) {
nextDir();
curRowIndex += 1;
}
}
return result;
};问题 12 :计数器 II
请你写一个函数 createCounter。这个函数接收一个初始的整数值 init。并返回一个包含三个函数的对象。
这三个函数是:
increment() 将当前值加 1 并返回。 decrement() 将当前值减 1 并返回。 reset() 将当前值设置为 init 并返回。 输入:init = 5, calls = ["increment","reset","decrement"] 输出:[6,5,4] 解释: const counter = createCounter(5); counter.increment(); // 6 counter.reset(); // 5 counter.decrement(); // 4
解析
js
var createCounter = function (init) {
let count = init;
return {
increment: () => ++count,
reset: () => (count = init),
decrement: () => --count,
};
// 使用代理的方式:
// let currentCount = init;
// return new Proxy(
// {},
// {
// get: (target, key) => {
// switch (key) {
// case "increment":
// return () => ++currentCount;
// case "decrement":
// return () => --currentCount;
// case "reset":
// return () => (currentCount = init);
// default:
// throw Error("Unexpected Method");
// }
// },
// }
// );
};问题 13: 扁平化嵌套数组
请你编写一个函数,它接收一个 多维数组 arr 和它的深度 n ,并返回该数组的 扁平化 后的结果。
多维数组 是一种包含整数或其他 多维数组 的递归数据结构。
数组 扁平化 是对数组的一种操作,定义是将原数组部分或全部子数组删除,并替换为该子数组中的实际元素。只有当嵌套的数组深度大于 n 时,才应该执行扁平化操作。第一层数组中元素的深度被认为是 0。
请在没有使用内置方法 Array.flat 的前提下解决这个问题。
js
/**
* @param {Array} arr
* @param {number} depth
* @return {Array}
*/
var flat = function (arr, n) {
// 方法1: 使用reduce+递归 效率最高
if (n === 0) return arr;
return arr.reduce((acc, cur) => {
if (Array.isArray(cur) && n > 0) {
acc.push(...flat(cur, n - 1));
} else {
acc.push(cur);
}
return acc;
}, []);
//循环 + 递归
let result = [];
for (let item of arr) {
if (Array.isArray(item) && n > 0) {
result.push(...flat(item, n - 1));
} else {
result.push(item);
}
}
return result;
};问题 14:函数防抖
请你编写一个函数,接收参数为另一个函数和一个以毫秒为单位的时间 t ,并返回该函数的 函数防抖 后的结果。
函数防抖 方法是一个函数,它的执行被延迟了 t 毫秒,如果在这个时间窗口内再次调用它,它的执行将被取消。你编写的防抖函数也应该接收传递的参数。
例如,假设 t = 50ms ,函数分别在 30ms 、 60ms 和 100ms 时调用。前两个函数调用将被取消,第三个函数调用将在 150ms 执行。如果改为 t = 35ms ,则第一个调用将被取消,第二个调用将在 95ms 执行,第三个调用将在 135ms 执行。 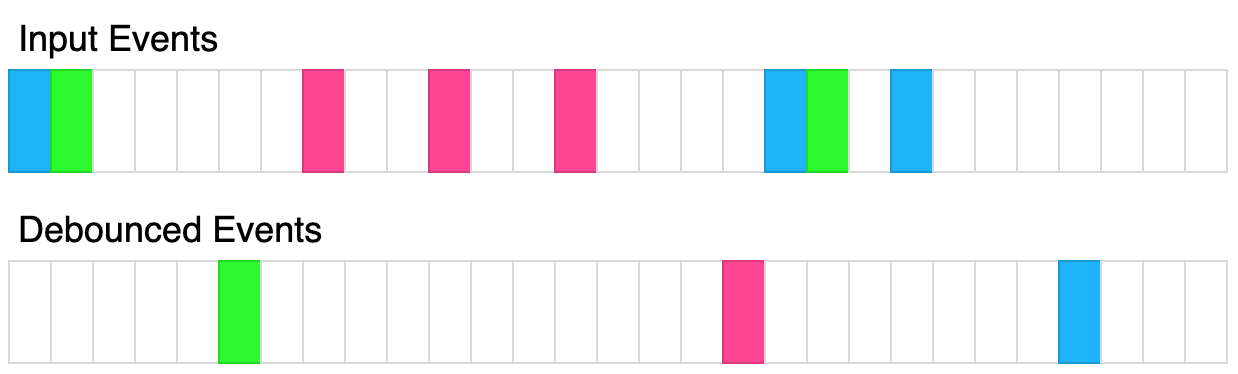
上图展示了了防抖函数是如何转换事件的。其中,每个矩形表示 100ms,反弹时间为 400ms。每种颜色代表一组不同的输入。
请在不使用 lodash 的 _.debounce() 函数的前提下解决该问题。
js
/**
* @param {Function} fn
* @param {number} t milliseconds
* @return {Function}
*/
var debounce = function (fn, t) {
let timer = null;
return function (...args) {
timer && clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn(...args);
}, t);
};
};问题 15:有时间限制的缓存
编写一个类,它允许获取和设置键-值对,并且每个键都有一个 过期时间 。
该类有三个公共方法:
set(key, value, duration) :接收参数为整型键 key 、整型值 value 和以毫秒为单位的持续时间 duration 。一旦 duration 到期后,这个键就无法访问。如果相同的未过期键已经存在,该方法将返回 true ,否则返回 false 。如果该键已经存在,则它的值和持续时间都应该被覆盖。
get(key) :如果存在一个未过期的键,它应该返回这个键相关的值。否则返回 -1 。
count() :返回未过期键的总数。
js
var TimeLimitedCache = function () {
this.cache = new Map();
};
/**
* @param {number} key
* @param {number} value
* @param {number} duration time until expiration in ms
* @return {boolean} if un-expired key already existed
*/
TimeLimitedCache.prototype.set = function (key, value, duration) {
let oldValue = this.cache.get(key);
oldValue && clearTimeout(oldValue.timerId);
// 也可以使用Date.now() + duration 替换setTimeout
let timerId = setTimeout(() => this.cache.delete(key), duration);
this.cache.set(key, { value, timerId });
return !!oldValue;
};
/**
* @param {number} key
* @return {number} value associated with key
*/
TimeLimitedCache.prototype.get = function (key) {
return this.cache.get(key)?.value ?? -1;
};
/**
* @return {number} count of non-expired keys
*/
TimeLimitedCache.prototype.count = function () {
return this.cache.size;
};问题 16:记忆函数
请你编写一个函数 fn,它接收另一个函数作为输入,并返回该函数的 记忆化 后的结果。
记忆函数 是一个对于相同的输入永远不会被调用两次的函数。相反,它将返回一个缓存值。
你可以假设有 3 个可能的输入函数:sum 、fib 和 factorial 。
sum 接收两个整型参数 a 和 b ,并返回 a + b 。假设如果参数 (b, a) 已经缓存了值,其中 a != b,它不能用于参数 (a, b)。例如,如果参数是 (3, 2) 和 (2, 3),则应进行两个单独的调用。 fib 接收一个整型参数 n ,如果 n <= 1 则返回 1,否则返回 fib (n - 1) + fib (n - 2)。 factorial 接收一个整型参数 n ,如果 n <= 1 则返回 1 ,否则返回 factorial(n - 1) * n 。
js
/**
* @param {Function} fn
* @return {Function}
*/
function memoize(fn) {
let cache = new Map();
return function (...args) {
let key = args.join(",");
if (cache.has(key)) {
return cache.get(key);
}
let result = fn(...args);
cache.set(key, result);
return result;
};
}问题 17:事件发射器
设计一个 EventEmitter 类。这个接口与 Node.js 或 DOM 的 Event Target 接口相似,但有一些差异。EventEmitter 应该允许订阅事件和触发事件。
你的 EventEmitter 类应该有以下两个方法:
subscribe - 这个方法接收两个参数:一个作为字符串的事件名和一个回调函数。当事件被触发时,这个回调函数将被调用。 一个事件应该能够有多个监听器。当触发带有多个回调函数的事件时,应按照订阅的顺序依次调用每个回调函数。应返回一个结果数组。你可以假设传递给 subscribe 的回调函数都不是引用相同的。 subscribe 方法还应返回一个对象,其中包含一个 unsubscribe 方法,使用户可以取消订阅。当调用 unsubscribe 方法时,回调函数应该从订阅列表中删除,并返回 undefined。 emit - 这个方法接收两个参数:一个作为字符串的事件名和一个可选的参数数组,这些参数将传递给回调函数。如果没有订阅给定事件的回调函数,则返回一个空数组。否则,按照它们被订阅的顺序返回所有回调函数调用的结果数组。
js
class EventEmitter {
eventMap = new Map();
/**
* @param {string} eventName
* @param {Function} callback
* @return {Object}
*/
subscribe(eventName, callback) {
let event = this.eventMap.get(eventName);
const id = Symbol();
const eventItem = {
id,
callback,
};
if (!event) {
this.eventMap.set(eventName, [eventItem]);
} else {
event.push(eventItem);
}
return {
unsubscribe: () => {
this.eventMap.set(
eventName,
this.eventMap.get(eventName).filter((item) => item.id !== id)
);
return undefined;
},
};
}
/**
* @param {string} eventName
* @param {Array} args
* @return {Array}
*/
emit(eventName, args = []) {
let event = this.eventMap.get(eventName);
if (!event) return [];
return event.map((item) => item.callback(...args));
}
}问题 18:记忆函数 II
现给定一个函数 fn ,返回该函数的一个 记忆化 版本。
一个 记忆化 的函数是一个函数,它不会被相同的输入调用两次。而是会返回一个缓存的值。
函数 fn 可以是任何函数,对它所接受的值类型没有任何限制。如果两个输入值在 JavaScript 中使用 === 运算符比较时相等,则它们被视为相同。
js
/**
* @param {Function} fn
* @return {Function}
*/
function memoize(fn) {
const idMap = new Map();
let id = 0;
const argsMap = new Map();
return function (...args) {
const idList = args.slice().map((arg) => {
if (idMap.has(arg)) {
return idMap.get(arg);
} else {
idMap.set(arg, ++id);
return id;
}
});
const key = JSON.stringify(idList);
console.log(idList, key, idMap);
if (argsMap.has(key)) {
return argsMap.get(key);
} else {
const res = fn(...args);
argsMap.set(key, res);
return res;
}
};
}问题 19:有时间限制的 Promise 对象
请你编写一个函数,它接受一个异步函数 fn 和一个以毫秒为单位的时间 t。它应根据限时函数返回一个有 限时 效果的函数。函数 fn 接受提供给 限时 函数的参数。
限时 函数应遵循以下规则:
如果 fn 在 t 毫秒的时间限制内完成,限时 函数应返回结果。 如果 fn 的执行超过时间限制,限时 函数应拒绝并返回字符串 "Time Limit Exceeded" 。
js
/**
* @param {Function} fn
* @param {number} t
* @return {Function}
*/
var timeLimit = function (fn, t) {
let timer = null;
return async function (...args) {
return new Promise(async (res, rej) => {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
rej("Time Limit Exceeded");
}, t);
fn(...args)
.then(res)
.catch(rej)
.finally(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
});
});
};
// 2: Promise Race
return async function (...args) {
return Promise.race([
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => reject("Time Limit Exceeded"), t);
}),
fn(...args),
]);
};
// 3: Promise
return async function (...args) {
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
const timeout = setTimeout(() => {
reject("Time Limit Exceeded");
}, t);
try {
const result = await fn(...args);
resolve(result);
} catch (err) {
reject(err);
}
clearTimeout(timeout);
});
};
};
/**
* const limited = timeLimit((t) => new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, t)), 100);
* limited(150).catch(console.log) // "Time Limit Exceeded" at t=100ms
*/问题 20:检查是否是类的对象实例
请你编写一个函数,检查给定的值是否是给定类或超类的实例。
可以传递给函数的数据类型没有限制。例如,值或类可能是 undefined 。
js
/**
* @param {*} obj
* @param {*} classFunction
* @return {boolean}
*/
var checkIfInstanceOf = function (obj, classFunction) {
if (obj === null || obj === undefined) return false;
let proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(obj);
while (proto) {
if (proto.constructor === classFunction) return true;
proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(proto);
}
return false;
};